Seefunge Pharmaceutical Technology
Seefunge Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. is a technology-based enterprise specializing in the transformation of ophthalmic research and industry incubation. The company focuses on the management of the entire lifecycle of the ophthalmic industry.
Business Segment
Seefunge Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.
R&D Center
Experienced talents in R&D and patent with international view
Commercial Center
Mature commercial platform
Manufacturing System
Complete MAH production quality management system
Innovative Pipeline
Products
Designed for people, Achieve by people
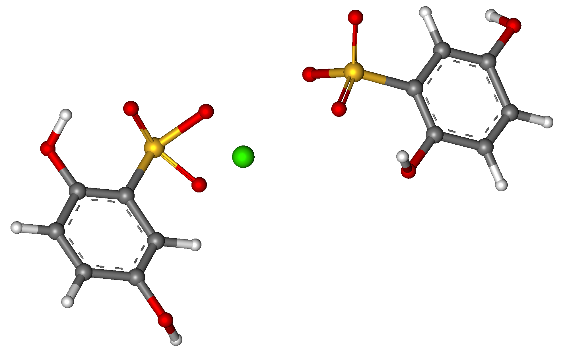
Calcium Dobesilate Tablet 250 mg
Composition: Calcium dobesilate monohydrate (250 mg) Indication: Microangiopathy (especially diabetic retinopathy), varicose symptom complex, haemorrhoidal complaints, microcirculation disorders.
Myopia
Myopia, also named near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is a common eye disease in which image of distant objects focuses in front of retina. As the result, the vision pattern is clear vision of close objects, but blurry vision of far objects. Myopia usually develops during childhood and adolescence. Then, it becomes stable between the ages of 20 and 40. Globally, the prevalence of myopia is nearly 2 billion people (more than 28.3% of the global population) and is growing rapidly, projected to reach 4.76 billion (49.8% of the global population) in 2050, while the prevalence of high myopia is expected to rise from the current 4.0% to 9.8%, nearly 1 billion people[1]. In East Asia and parts of South-East Asia, the prevalence of both myopia and high myopia was high (47.0%), much higher than Central Europe (27.1%), Central Asia (17.0%), and Central Africa (7.0%)[2].
Besides the main symptom, myopia also exhibits other symptoms, including headaches, eyestrain, and squint or partially close the eyelids to see clearly. Severe myopia, increased risk of retinal detachment, glaucoma, cataracts, and other serious eye pathologies. Normally, a basic eye exam can confirm myopia. And a series of exam schedule could monitor myopia progression and other complications. Current medical corrections are quite limited, such as the eyeglasses, contact lenses or refractive surgery. However, the efficacy and safety among the above are unsatisfactory.
The novel ophthalmic medicine treatment (low-dose atropine sulfate eye drops) is the only drug verified by evidence-based medicine to effectively delay the progression of myopia of children and adolescents.
Non-infectious Ocular Inflammation
Abnormal inflammations without microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungus, parasites, etc.) infection are common ocular pathologies exhibiting symptoms of swelling, pain, and redness. Pathologically, the imbalance of inflammatory homeostasis within the ocular microenvironment is caused by abnormal secretion of inflammatory cytokines, T-cell infiltration, overactivation of the complement immune system (innate immunity), chronic oxidative stress, neovascularization, allergy, irritation, and tissue injury of surgeries, etc. Thus, non-infectious ocular inflammation is the underlying link associated with multiple ocular diseases and conditions, including dry eye (DED), peri-surgery treatment, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), uveitis, conjunctivitis, etc. As public health improves, non-infectious ocular anti-inflammation emerges as a huge clinical need.
NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a family of therapeutic drug classes, which is used to ease pain, anti-inflammation, reduce fever, and antiplatelet aggregation. Namely, the non-steroidal is intended to distinguish from the conventional anti-inflammatory corticosteroids because of severe side effects, especially the increase of IOP (intraocular pressure). Generally, the administration of NSAIDs is safe for short-term use, but long-term use could evoke an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, kidney disease, and anemia caused by hindrance of erythropoietin synthesis. NSAIDs specifically inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isoenzymes). They are upstream masters of inflammatory biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which result in inflammation and thromboxane for blood clotting. The most prominent NSAIDs are aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen aiming at the treatment of acute or chronic pain and inflammation of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, tissue injury, headache, migraine, macular edema, etc.
However, the inflammation pathology is mainly associated with COX-2 and COX-1 for the gastrointestinal side effects. Thus, the evolving trend is emerging from the original non-selective type to COX-2 selective. As a result, the pharmacological pattern changes to fewer gastrointestinal side effects but promotes thrombosis, and increased risk of heart attack. Since the doctrine of the mean is the key, the balance of selectivity is the most vital characteristic for optimal application targeting a specific disease.
Currently, the scientific categories of NSAIDs reference to molecular structure and selectivity include acetylated salicylates (aspirin), non-acetylated salicylates (diflunisal, salsalate), anthranilic acids (meclofenamate and mefenamic acid), propionic acids (naproxen and ibuprofen), enolic acids (meloxicam and piroxicam), acetic acids (diclofenac and indomethacin), naphthylalanine (nabumetone), and selective COX-2 inhibitors (celecoxib, etoricoxib).
Pranoprofen, bromfenac sodium, and other prominent NSAIDs applied as eye drops belong to the non-selective COX inhibitors, which can inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2. These medicines may lead to a higher incidence of ocular adverse effects reported after their administration, such as sensation of ocular irritation, conjunctival congestion and inflammation, corneal erosions and superficial keratitis, blepharitis, itchy and swollen eyelids, and discomfort such as ophthalmoplegia. In contrast, highly selective inhibitors of COX-2 similar to meloxicam, (e.g., indomethacin eye drops, etc.) have reported only transient burning and stinging, tearing, etc., and no occurrence of corneal inflammatory injury, conjunctival inflammatory injury, or eyelid swelling. Therefore, the COX-2-inclined NSAIDs exhibit massive potential to be applied in ophthalmic treatment.